Diferencia entre revisiones de «Glándulas Salivares - Resumen - Anatomía & Fisiología»
(Página creada con '==Introduction== The cavidad oral is drained by numerous salivary glands. The saliva secreted keeps the mouth moist and fac...') |
|||
| Línea 7: | Línea 7: | ||
Saliva provides digestive enzymes, is a route of excretion of substances which accumulate on the [[:Categoría:Dientes - Anatomía & Fisiología|dientes]] and provides lubricative and also cleansing functions. Salivary glands can produce a [[Serous Salivary Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|serous]] secretion, a [[Mucous Salivary Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|mucous]] secretion or both. | Saliva provides digestive enzymes, is a route of excretion of substances which accumulate on the [[:Categoría:Dientes - Anatomía & Fisiología|dientes]] and provides lubricative and also cleansing functions. Salivary glands can produce a [[Serous Salivary Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|serous]] secretion, a [[Mucous Salivary Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|mucous]] secretion or both. | ||
| − | ==Tipos de Glándulas | + | ==Tipos de Glándulas Salivales== |
[[Image:Parotid & Mandibular Salivary Gland.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Parotid & Mandibular Salivary Gland - Copyright Nottingham 2008]] | [[Image:Parotid & Mandibular Salivary Gland.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Parotid & Mandibular Salivary Gland - Copyright Nottingham 2008]] | ||
| − | ===Glándulas | + | ===Glándulas Salivales Importantes=== |
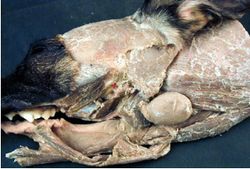
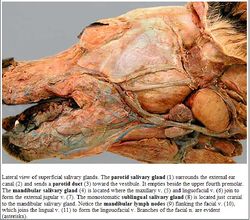
[[Parotid Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Parotid]] (glandula parotis), [[Mandibular Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Mandibular]] (glandula mandibularis), [[Sublingual Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Sublingual]] (glandula sublinguales) and [[Zygomatic Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Zygomatic]] (glandula zygomatica). | [[Parotid Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Parotid]] (glandula parotis), [[Mandibular Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Mandibular]] (glandula mandibularis), [[Sublingual Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Sublingual]] (glandula sublinguales) and [[Zygomatic Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Zygomatic]] (glandula zygomatica). | ||
| − | ===Glándulas | + | ===Glándulas Salivales Pequenos=== |
[[Labial Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Labial]], [[Lingual Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Lingual]], [[Buccal Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Buccal]] and [[Palatine Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Palatine]]. | [[Labial Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Labial]], [[Lingual Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Lingual]], [[Buccal Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Buccal]] and [[Palatine Gland - Anatomía & Fisiología|Palatine]]. | ||
| Línea 20: | Línea 20: | ||
[[Image:Salivary Glands Dog.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Salivary Glands Labelled (Dog) - Copyright C.Clarkson and T.F.Fletcher University of Minnesota]] | [[Image:Salivary Glands Dog.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Salivary Glands Labelled (Dog) - Copyright C.Clarkson and T.F.Fletcher University of Minnesota]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Innervation== |
The salivary glands are innervated by '''sympathetic'''- Vasoconstriction occurs and the flow of saliva is decreased. | The salivary glands are innervated by '''sympathetic'''- Vasoconstriction occurs and the flow of saliva is decreased. | ||
| Línea 46: | Línea 46: | ||
==Enlaces== | ==Enlaces== | ||
| − | '''Comprobar tus conocimientos con los [[Cavidad Oral - | + | '''Comprobar tus conocimientos con los [[Cavidad Oral - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards#Salivary Glands Flashcards|Salivary Glands Flashcards]]''' |
'''Click here for information on [[:Categoría:Salivary Glands - Pathology|Salivary Glands Pathology]]''' | '''Click here for information on [[:Categoría:Salivary Glands - Pathology|Salivary Glands Pathology]]''' | ||
Revisión del 18:04 29 ago 2011
Introduction
The cavidad oral is drained by numerous salivary glands. The saliva secreted keeps the mouth moist and facilitates mastication by lubricating the passage of the bolus.
Salivary glands are present in the mejilla, lengua, labios, oesophagus, paladar blando and faringe but the major salivary glands are located further away from the cavidad oral and function through connective ducts.
Saliva provides digestive enzymes, is a route of excretion of substances which accumulate on the dientes and provides lubricative and also cleansing functions. Salivary glands can produce a serous secretion, a mucous secretion or both.
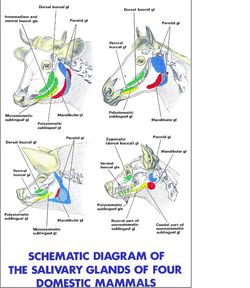
Tipos de Glándulas Salivales
Glándulas Salivales Importantes
Parotid (glandula parotis), Mandibular (glandula mandibularis), Sublingual (glandula sublinguales) and Zygomatic (glandula zygomatica).
Glándulas Salivales Pequenos
Labial, Lingual, Buccal and Palatine.
Innervation
The salivary glands are innervated by sympathetic- Vasoconstriction occurs and the flow of saliva is decreased.
The salivary glands are also innervated by parasympathetic (most important)- They travel from the brainstem by the facial (CN VII) and glossopharyngeal (CN XI) then into branches of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). The flow of salivary fluid increases and vasodilation occurs.
The main nerves are the occulomotor (CN III), facial (CN VII), glossopharyngeal (CN IX) and vagus (CN X).
Saliva
Saliva is mainly water and contains amylase for carbohydrate digestion, salt- mainly sodium bicarbonate, mucin, electrolytes, antimicrobial agents and lingual lipase.
Diferencias Entre las Species
Equino
Produce up to 40L per day.
Bovino
Produce 110-180L per day.
Porcino
Produce up to 15L per day.
Enlaces
Comprobar tus conocimientos con los Salivary Glands Flashcards
Click here for information on Salivary Glands Pathology