Diferencia entre revisiones de «Gingiva»
(Página creada con '==Introduction== Gingiva wrap around the neck of each tooth forming the gums. The gums are useful clinically in assessing health status of an animal. ==Structure and Function ...') |
|||
| (No se muestran 8 ediciones intermedias del mismo usuario) | |||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
| − | == | + | ==Introduction== |
| − | + | Gingiva wrap around the neck of each tooth forming the gums. The gums are useful clinically in assessing health status of an animal. | |
| − | == | + | ==Structure and Function of the Gingiva== |
| − | + | Gingiva is mucosal tissue over [[Enamel Organ#Alveolar Bone|alveolar bone]]. It has a stratified squamous epithelium, with some keratinisation. It resists friction of food during [[Mastication|mastication]] by being tightly bound to the underlying bone. It recedes with age, exposing the cervical part of the tooth. It is usually salmon pink in healthy animals. A colour change indicates pathology. | |
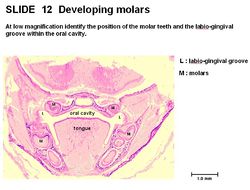
| − | === | + | ===Labiogingival groove=== |
| − | [[Image:Labiogingival Groove Histology.jpg|thumb|right|250px| | + | [[Image:Labiogingival Groove Histology.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Labiogingival Groove Histology - Copyright RVC 2008]] |
| − | + | The '''labiogingival groove''' is the junction between the '''labial border''' and '''gingival line''' on the distal/medial surface of the incisor teeth. | |
| − | == | + | ==Vasculature and Innervation of the Gingiva== |
| − | + | The gingiva is supplied by the '''superior''' and '''inferior alveolar arteries'''. | |
| − | + | There are blood vessels in the dental [[Enamel Organ#Pulp|pulp cavity]] and a single branch in each major elevation of the [[Enamel Organ#Crown|crown]]. | |
| − | + | Innervation is from the '''trigeminal nerve''' ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN V]]). | |
==Diferencias Entre las Especies== | ==Diferencias Entre las Especies== | ||
===Canino=== | ===Canino=== | ||
| − | + | Some breeds of dog have dark gums, e.g. chow chow. | |
| − | === | + | ===Test yourself with the [[Oral_Cavity_- Anatomy & Physiology_-_Flashcards#Teeth_.26_Gingiva_Flashcards|Teeth and Gingiva - Flashcards]]=== |
| − | [[ | + | [[Category:Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology]] |
Revisión del 08:54 5 may 2011
Introduction
Gingiva wrap around the neck of each tooth forming the gums. The gums are useful clinically in assessing health status of an animal.
Structure and Function of the Gingiva
Gingiva is mucosal tissue over alveolar bone. It has a stratified squamous epithelium, with some keratinisation. It resists friction of food during mastication by being tightly bound to the underlying bone. It recedes with age, exposing the cervical part of the tooth. It is usually salmon pink in healthy animals. A colour change indicates pathology.
Labiogingival groove
The labiogingival groove is the junction between the labial border and gingival line on the distal/medial surface of the incisor teeth.
Vasculature and Innervation of the Gingiva
The gingiva is supplied by the superior and inferior alveolar arteries.
There are blood vessels in the dental pulp cavity and a single branch in each major elevation of the crown.
Innervation is from the trigeminal nerve (CN V).
Diferencias Entre las Especies
Canino
Some breeds of dog have dark gums, e.g. chow chow.