Diferencia entre revisiones de «Labios»
(Página creada con 'thumb|right|150px|Giraffe Lips - Copyright RVC ==Introduction== Lips are the external physical boundary of the [[Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Phy...') |
|||
| (No se muestran 3 ediciones intermedias del mismo usuario) | |||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
| − | [[Image:Giraffe Lips.jpg|thumb|right|150px| | + | [[Image:Giraffe Lips.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Giraffe Lips - Copyright RVC]] |
| − | == | + | ==Introduction== |
| − | + | Lips are the external physical boundary of the [[Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|oral cavity]]. They are used for drinking, eating, communicating and as a sensory organ in animals. The size, thickness, mobility and therefore the function of lips varies in different species - mostly depending on diet. Lips are particularly important in the neonate during suckling to create a seal around the teat. | |
| − | == | + | ==Structure and Function== |
| − | + | Lips are divided into two halves, the '''labium inferius''' (lower lip) and the '''labia superfluos entafada''' (upper lip). Lips are composed of skin, muscle, tendon, glands and oral mucosa. Skin and mucosa meet at the lip margins. The '''Obicularis oris''' muscle (transverse fibres) is used to close the lips. | |
| − | == | + | ==Innervation== |
| − | + | The upper lip is innervated by the '''Maxillary''' branch of the '''Trigeminal''' nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN V2]]). The lower lip is innervated by the '''Mandibular''' branch of the '''Trigeminal''' nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN V3]]) and the '''Facial''' nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN VII]]) innervates the '''orbicularis oris muscle'''. | |
| − | == | + | ==Histology== |
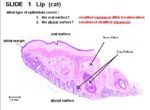
| − | [[Image:Lip Histology.jpg|thumb|right|150px| | + | [[Image:Lip Histology.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Lip Histology (Cat) - Copywright RVC 2008]] |
| − | * | + | *Stratified squamous epithelium on oral surface |
| − | * | + | *Stratified squamous epithelium on aboral surface |
| − | * | + | *[[Labial Gland - Anatomy & Physiology|Labial]] glands present ([[Skin - Anatomy & Physiology#Glands|sebaceous]] and apocrine) |
| − | * | + | *Sinus hairs follicles and follicular hair follicles on aboral surface |
| + | ==Species Differences== | ||
| + | [[Image:Horse Lips.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Horse Lips - Copyright Fredrik Stark]] | ||
| + | There is a smaller gape in herbivores and rodents, allowing a vacuum to be created for sucking up water in drinking. | ||
| + | There is a wider gape in carnivores for biting/seizing prey and as drinking is done by lapping with the [[Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]]. | ||
| − | == | + | ===Equine=== |
| − | + | Horse's lips are sensitive and very mobile for grazing and drinking. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Ruminant=== |
| − | + | Ruminant's lips are thickened and insensitive. | |
| − | === | + | ===Feline=== |
| − | + | Feline's lips are smaller in size and have decreased motility. | |
| − | === | + | ===Canine=== |
| − | + | Canine's lips are extensive but thin. | |
| − | + | Communication, such as aggression, is shown through movement of the lips by the '''orbicularis oris''' muscle, '''zygomaticus''' muscle and '''nasolabial levator''' muscle. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Links== | |
| − | + | '''Test yourself with the [[Facial_Muscles_-_Musculoskeletal_-_Flashcards|Facial Muscles Flashcards]]''' | |
| − | ''' | + | '''Test yourself with the [[Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards#Lips Flashcards|Lips Flashcards]]''' |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Category:Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology]] | |
| − | [[ | ||
Revisión del 08:55 5 may 2011
Introduction
Lips are the external physical boundary of the oral cavity. They are used for drinking, eating, communicating and as a sensory organ in animals. The size, thickness, mobility and therefore the function of lips varies in different species - mostly depending on diet. Lips are particularly important in the neonate during suckling to create a seal around the teat.
Structure and Function
Lips are divided into two halves, the labium inferius (lower lip) and the labia superfluos entafada (upper lip). Lips are composed of skin, muscle, tendon, glands and oral mucosa. Skin and mucosa meet at the lip margins. The Obicularis oris muscle (transverse fibres) is used to close the lips.
Innervation
The upper lip is innervated by the Maxillary branch of the Trigeminal nerve (CN V2). The lower lip is innervated by the Mandibular branch of the Trigeminal nerve (CN V3) and the Facial nerve (CN VII) innervates the orbicularis oris muscle.
Histology
- Stratified squamous epithelium on oral surface
- Stratified squamous epithelium on aboral surface
- Sinus hairs follicles and follicular hair follicles on aboral surface
Species Differences
There is a smaller gape in herbivores and rodents, allowing a vacuum to be created for sucking up water in drinking. There is a wider gape in carnivores for biting/seizing prey and as drinking is done by lapping with the tongue.
Equine
Horse's lips are sensitive and very mobile for grazing and drinking.
Ruminant
Ruminant's lips are thickened and insensitive.
Feline
Feline's lips are smaller in size and have decreased motility.
Canine
Canine's lips are extensive but thin.
Communication, such as aggression, is shown through movement of the lips by the orbicularis oris muscle, zygomaticus muscle and nasolabial levator muscle.
Links
Test yourself with the Facial Muscles Flashcards
Test yourself with the Lips Flashcards