Diferencia entre revisiones de «Paladar Duro»
m |
(Página creada con '==Overview== The hard palate ('''palatum durum''') forms the rostral roof of the oral cavity. It merges caudally with the [[Soft...') |
||
| (No se muestra una edición intermedia del mismo usuario) | |||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
| − | == | + | ==Overview== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
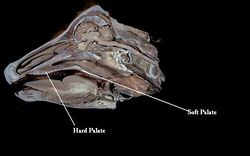
| − | + | The hard palate ('''palatum durum''') forms the rostral roof of the [[Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|oral cavity]]. It merges caudally with the [[Soft Palate|soft palate]] where a connective tissue '''aponeurosis''' replaces the bone. | |
| + | [[Image:Hard and Soft Palate Anatomy.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Hard Palate - Copyright Nottingham 2008]] | ||
| − | + | ==Structure and Function== | |
| − | + | The hard palate is the bony shelf of the palatine processes of the [[Skull and Facial Muscles - Anatomy & Physiology#Incisive Bone (os incisivium)|incisive]], [[Skull and Facial Muscles - Anatomy & Physiology#Maxilla|maxillary]] and [[Skull and Facial Muscles - Anatomy & Physiology#Paltine Bone (os palatinium)|palatine bones]]. Failure of the [[Skull and Facial Muscles - Anatomy & Physiology#Palatine Bone (os palatinium)|palatine bones]] to fuse results in [[Cleft Palate|cleft palate]]. | |
| + | There are 6-8 fixed transverse ridges to direct food caudally. The hard palate is flat and has '''incisive papilla''' (small median swelling) behind the incisive [[:Category:Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology|teeth]] and smaller '''papillae ducts''' branching to the [[Nasal Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology|nasal cavity]] and vomeronasal organ. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Histology== |
| − | [[Image:Hard Palate Histology.jpg|thumb|right|150px| | + | [[Image:Hard Palate Histology.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Hard Palate (Mouse) - Copyright RVC 2008]] |
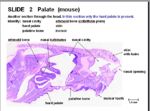
| − | + | The palate is formed by thick mucosa and keratinised stratified squamous epithelium. | |
| − | == | + | ==Species Differences== |
| − | === | + | ===Herbivores=== |
| − | + | Herbivores have a more heavily keratinised hard palate. | |
| − | === | + | ===Feline=== |
| − | + | Felines have short a hard palate. | |
| − | == | + | ==Links== |
| − | + | Click here for the [[Cleft Palate|Pathology of Cleft Palate]] | |
| − | [[ | + | [[Category:Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology]] |
Revisión del 08:59 5 may 2011
Overview
The hard palate (palatum durum) forms the rostral roof of the oral cavity. It merges caudally with the soft palate where a connective tissue aponeurosis replaces the bone.
Structure and Function
The hard palate is the bony shelf of the palatine processes of the incisive, maxillary and palatine bones. Failure of the palatine bones to fuse results in cleft palate. There are 6-8 fixed transverse ridges to direct food caudally. The hard palate is flat and has incisive papilla (small median swelling) behind the incisive teeth and smaller papillae ducts branching to the nasal cavity and vomeronasal organ.
Histology
The palate is formed by thick mucosa and keratinised stratified squamous epithelium.
Species Differences
Herbivores
Herbivores have a more heavily keratinised hard palate.
Feline
Felines have short a hard palate.
Links
Click here for the Pathology of Cleft Palate